

Thus, the importance of agroforestry systems (AFS) is the land-use management. Agricultural lands are believed to be a major potential carbon sink to absorb large quantities of carbon if trees are reintroduced with judiciously managed crops and/or animals (Albrecht and Kandji, 2003).
#Carbon sequestration rate free
In addition, many agricultural lands are left fallow and not used for food production in some developed countries due to local development and free trade agreements. One example is the Ex-Mega Rice Project (EMRP) in Indonesia where an area of around 146 million ha of peat swamp forest was converted to rice ( Oryza sativa), palm ( Elaeis guineensis)-oil production and settlement in the 1980s (Galudra et al., 2010). Many forests have been cut down to make room for cultivation and to increase food or energy crops production in developing countries. Land use has changed around the world in the last few decades.
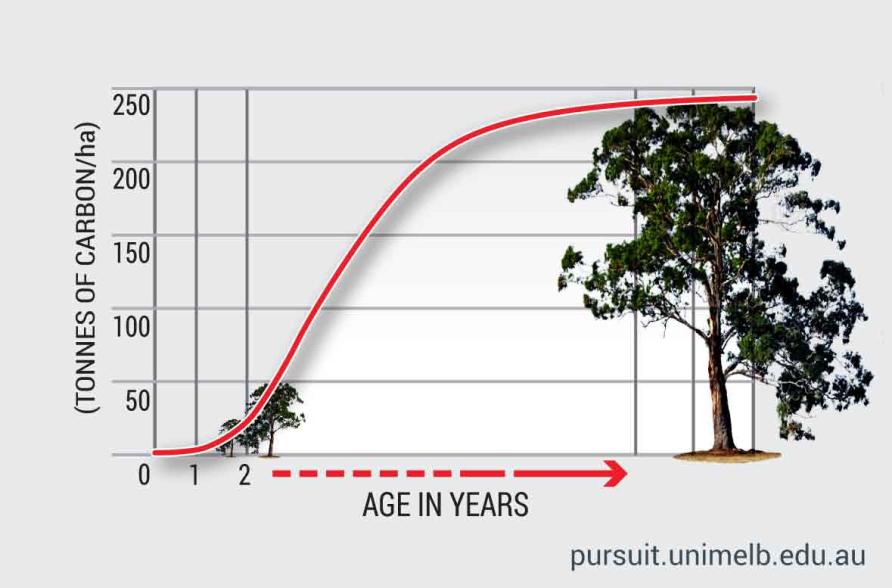
Keywords: Taiwan, plantation on farm land, carbon capture and storage, aboveground biomass, forest management Net present value of afforestation for a 20-year period of carbon or wood management is estimated at around US$ 30,000 given an annual base interest rate of 3 %. As a result of changing the farming systems to hardwood forest in this study area, carbon sequestration and carbon storage have increased at the rate of 2.98 t C ha - 1 year - 1. Sugarcane production does not contribute significantly to carbon sequestration, because almost all the cane fiber is used as fuel for sugar mills.

Carbon sequestration from rice ( Oryza sativa) or sugarcane ( Saccharum officinarum) production is discharged as a result of straw decomposition in the soil which also improves soil quality. If this amount of carbon dioxide were exchanged on the Chicago Climate Exchange (CCX) market, the income earned would be 821 US$ ha - 1. An estimated carbon sequestration of 11,254 t C was observed for a 189ha-hardwood forest which is equivalent to 41,264 t CO 2. Through pilot tests run on an age-volume model, an estimation bias was obtained and used to correct predicted volume estimates for a farm forest over a 20-year period. The quantity of sequestrated carbon was determined based on aboveground biomass. In this study, carbon sequestration and wood production were evaluated on afforested farms by integrating the Gaussian diameter distribution model and exponential diameter-height model derived from sample plots of an afforested hardwood forest in Taiwan. In the last few decades, many forests have been cut down to make room for cultivation and to increase food or energy crops production in developing countries. of Forestry and Natural Resources, 300 University Road - 60004 - Chiayi - Taiwan Taiwan plantation on farm land carbon capture and storage aboveground biomass forest managementĬomparison of carbon sequestration potential in agricultural and afforestation farming systems As a result of changing the farming systems to hardwood forest in this study area, carbon sequestration and carbon storage have increased at the rate of 2.98 t C ha- 1 year- 1. Carbon sequestration from rice (Oryza sativa) or sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum) production is discharged as a result of straw decomposition in the soil which also improves soil quality. If this amount of carbon dioxide were exchanged on the Chicago Climate Exchange (CCX) market, the income earned would be 821 US$ ha- 1. An estimated carbon sequestration of 11,254 t C was observed for a 189ha-hardwood forest which is equivalent to 41,264 t CO2.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
